
On April 27, a bi-partisan bill was introduced in the U.S. Senate to amend the Foreign Agents Registration Act of 1938 (FARA). Senate Bill 1364, the Foreign Agents Disclosure and Registration Enhancement Act, would provide the Attorney General with greater […]
On April 27, a bi-partisan bill was introduced in the U.S. Senate to amend the Foreign Agents Registration Act of 1938 (FARA).
Senate Bill 1364, the Foreign Agents Disclosure and Registration Enhancement Act, would provide the Attorney General with greater authority to promote enforcement of disclosure requirements for agents of foreign principals and increases penalties for noncompliance.
The bill also “improves FARA advisory opinion transparency and requires the Government Accountability Office to study whether and to what extent the Lobbying Disclosure Act exemption is being abused to conceal foreign lobbying activity,” according to the press release of U.S. Senator Chuck Grassley, the lead Republican sponsor of the bill.
Identical legislation had been introduced in 2019 but did not pass.
December 14, 2021 •
U.S. DOJ Seeks Input on New FARA Rulemaking

The Robert F. Kennedy Department of Justice Building
On December 13, the U.S. Department of Justice (DOJ) formally requested public input regarding future implementation of Foreign Agents Registration Act (FARA) regulations. The regulations have not been amended in 14 years. The DOJ’s Advance Notice of Proposed Rulemaking was […]
On December 13, the U.S. Department of Justice (DOJ) formally requested public input regarding future implementation of Foreign Agents Registration Act (FARA) regulations.
The regulations have not been amended in 14 years.
The DOJ’s Advance Notice of Proposed Rulemaking was published in the Federal Register, Vol. 86, No. 236, seeking public comment to help inform the DOJ’s decision-making prior to its issuance of any new proposed FARA regulations. The DOJ’s National Security Division anticipates issuing a Notice of Proposed Rulemaking that would amend or otherwise clarify the scope of certain exemptions, update various definitions, and make other modernizing changes to the Attorney General’s FARA implementing regulations.
The public comment period ends on February 11, 2022.
January 20, 2021 •
Trump Revokes Executive Order Concerning Ethics for Appointees

The White House - AgnosticPreachersKid
On his last full day in office, President Trump revoked an executive order concerning governmental ethics and, in effect, removed barriers for former officials to lobby the United States government immediately. On January 19, President Trump signed an Executive Order […]
On his last full day in office, President Trump revoked an executive order concerning governmental ethics and, in effect, removed barriers for former officials to lobby the United States government immediately. On January 19, President Trump signed an Executive Order fully revoking his prior Executive Order from 2017, which mandated ethic commitments for executive branch appointees.
On January 28, 2017, President Donald J. Trump signed Executive Order 13770, Ethics Commitments by Executive Branch Appointees, which prohibited appointees of the Executive Branch from lobbying the agency they were appointed to serve for five years after leaving office. Additionally, they would be permanently prohibited from engaging on behalf of any foreign government or foreign political party if it would require them to register under the Foreign Agents Registration Act.
The executive order is effective at noon when President-elect Joe Biden is sworn into office. Those prohibitions will no longer exist under President Trump’s 2017 Executive Order. The early order also prohibited appointees from accepting gifts, with limited exceptions, from registered lobbyists and lobbying organizations for the duration of their service as appointees. Also, registered lobbyists appointed to an executive agency could not participate in matters in which they lobbied for two years after the date of their appointment.
This 2017 Executive Order had superseded and revoked a similar Executive Order signed by former President Barack Obama in 2009.
December 2, 2020 •
Fossil Fuel Companies Won’t Be Powering Biden’s Inauguration

U.S. Capitol - by Martin Falbisoner
President-elect Joe Biden’s newly formed inauguration committee will not be accepting contributions from registered federal lobbyists, foreign agents registered under the Foreign Agent Registration Act, or from fossil fuel companies, their executives, or PACs organized by them. The Biden Inaugural […]
President-elect Joe Biden’s newly formed inauguration committee will not be accepting contributions from registered federal lobbyists, foreign agents registered under the Foreign Agent Registration Act, or from fossil fuel companies, their executives, or PACs organized by them.
The Biden Inaugural Committee, a 501(c)(4) non-profit entity named PIC 2021, Inc., will still accept contributions from American corporate entities and associations to fund the celebratory events of the January 20, 2021 inauguration.
The contributions, which are not tax deductible as charitable contributions for federal income tax purposes, will also be accepted from labor organizations, U.S. citizens, and lawfully admitted permanent residents.
An inaugural committee is responsible for activities connected with the inaugural ceremony, except for the swearing-in ceremony at the Capitol and a luncheon honoring the president and vice president.
Contributions to an inaugural committee are not subject to any contribution limits.

U.S. Capitol - by Martin Falbisoner
On October 23, legislation was introduced in the U.S. Congress to amend and expand the Foreign Agents Registration Act to compel lobbyists for Chinese companies to register as foreign agents. The Chinese Communist Party Influence Transparency Act, introduced as identical […]
On October 23, legislation was introduced in the U.S. Congress to amend and expand the Foreign Agents Registration Act to compel lobbyists for Chinese companies to register as foreign agents.
The Chinese Communist Party Influence Transparency Act, introduced as identical bills in both houses of Congress by Rep. Mike Gallagher and Sen. Tom Cotton, would repeal the exemption from registration for persons, acting as agents of a covered Chinese business organization, providing private and nonpolitical representation of trade and commercial interests.
House Bill 8663 and Senate Bill 4843 would also remove the exemption for persons filing disclosure reports under the Lobbying Disclosure Act of 1995 in connection with the representation of business organizations organized under the laws of, or having their principal place of business in, the People’s Republic of China. The bill defines a covered Chinese business organization as an entity designated by the Attorney General as subject to the extrajudicial direction of the Chinese Communist Party or an entity organized under the laws of, or having its principal place of business in, the People’s Republic of China (including any subsidiary or affiliate of such an entity).
The legislation would become effective 180 days after enactment.
June 5, 2020 •
DOJ FARA Unit Publishes Letters of Determination

The Robert F. Kennedy Department of Justice Building
On June 4, the Foreign Agents Registration Acts (FARA) Unit of the Department of Justice (DOJ) updated its public list “Letters of Determination” it has issued since 2017. The list was initially published on the DOJ’s website on June 1. […]
On June 4, the Foreign Agents Registration Acts (FARA) Unit of the Department of Justice (DOJ) updated its public list “Letters of Determination” it has issued since 2017. The list was initially published on the DOJ’s website on June 1.
The 15 letters made public were sent by the FARA Unit to potential registrants after evaluations were completed by the unit to determine whether registration was required. The letters, issued between 2017 and 2019, set forth relevant facts, applicable statutory and regulatory provisions, and the unit’s analysis.
While the names of the individuals and foreign principals who are the subject of the letters, and their respective activities being considered by the FARA Unit, are not redacted, the letters do contain some redactions.
According to the FARA Unit, “[The FARA Unit of the DOJ] regularly reviews information to determine whether an entity or individual has an obligation to register under FARA. Where such information suggests that a registration obligation may exist, the FARA Unit sends a letter advising the entity or individual of its potential obligations under FARA, and seeking additional information.”
FARA is a disclosure statute requiring persons acting as agents of foreign principals in a political or quasi-political capacity to make public disclosure of their relationship with and activities for the foreign principal.
February 3, 2020 •
Bill to Amend FARA Introduced to help Enforcement

On January 30, a bill was introduced in the U.S. House of Representatives to amend the Foreign Agents Registration Act (FARA) to help its enforcement. House Bill 5733, introduced by Rep. Seth Moulton, would waive the application of the FARA […]
On January 30, a bill was introduced in the U.S. House of Representatives to amend the Foreign Agents Registration Act (FARA) to help its enforcement.
House Bill 5733, introduced by Rep. Seth Moulton, would waive the application of the FARA law to agents representing foreign enterprises not under the control or direction of foreign governments or foreign political parties.
In his press release, Moulton argues the legislation would make it easier to enforce FARA by narrowing those who must register as foreign agents to include only those people working on behalf of foreign governments or foreign political parties.
The legislation would also exclude agents who represent foreign governments engaging in a pattern of gross violations of human rights from an exemption currently provided under the Act for agents engaged in scholastic and certain other pursuits and would add civil penalties for violations.
September 27, 2019 •
FARA Update eFiling Registration System
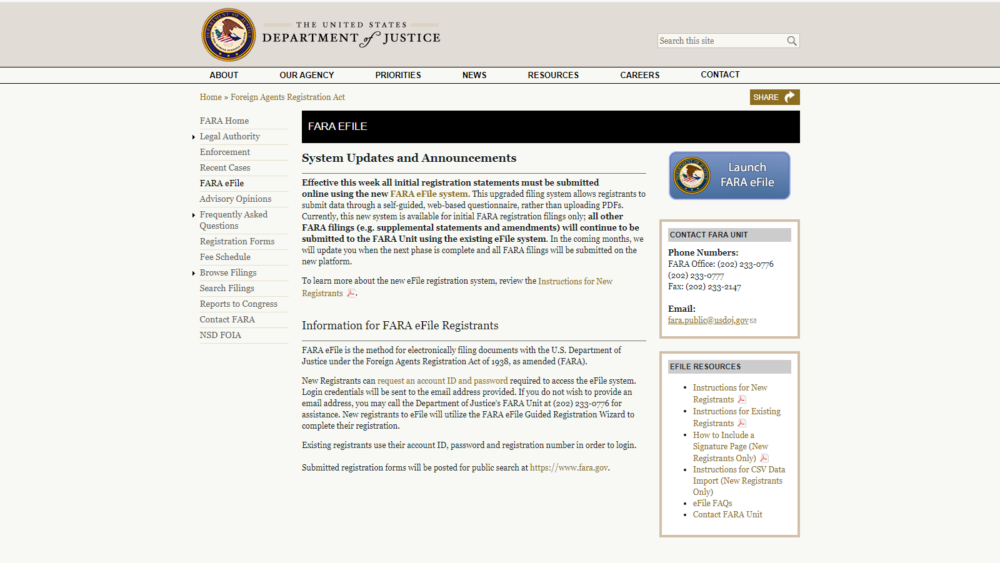
The U.S. Department of Justice (DOJ) announced, effective this week, all foreign agents filing with the DOJ under the Foreign Agents Registration Act (FARA) must submit their initial registration statements using its new online eFile system. In the DOJ’s announcement, […]
The U.S. Department of Justice (DOJ) announced, effective this week, all foreign agents filing with the DOJ under the Foreign Agents Registration Act (FARA) must submit their initial registration statements using its new online eFile system.
In the DOJ’s announcement, the agency said the “upgraded filing system allows registrants to submit data through a self-guided, web-based questionnaire, rather than uploading PDFs.”
While the current system will only allow for initial registrations, all other FARA filings will continue to use the existing eFiling system until further notice.
FARA is a disclosure statute requiring persons acting as agents of foreign principals in a political or quasi-political capacity to make public disclosure of their relationship with and activities for the foreign principal.
June 17, 2019 •
NYCU Video Digest – June 17, 2019
New FARA Regulations, and changes being made to lobbying disclosures in various states. Catch up with all of it in this edition of News You Can Use Video Digest!
New FARA Regulations, and changes being made to lobbying disclosures in various states. Catch up with all of it in this edition of News You Can Use Video Digest!
June 11, 2019 •
Bi-Partisan Bill to Amend FARA Introduced in U.S. Senate

On June 10, a bi-partisan bill was introduced in the U.S. Senate to amend the Foreign Agents Registration Act of 1938 (FARA). The bill would provide the U.S. Attorney General greater authority to promote enforcement of the law and increase […]
On June 10, a bi-partisan bill was introduced in the U.S. Senate to amend the Foreign Agents Registration Act of 1938 (FARA).
The bill would provide the U.S. Attorney General greater authority to promote enforcement of the law and increase disclosure requirements of agents of foreign principals.
Senate Bill 1762 requires foreign agents to disclose their clients immediately so policy makers can evaluate their positions in light of those associations.
Additionally, the bill requires the Justice Department to craft a comprehensive FARA enforcement strategy, and creates oversight mechanisms to prevent abuse of the new authorities according to the press release of U.S. Senator Chuck Grassley, the Republican sponsor of the bill.
The legislation would also establish a review of the Lobbying Disclosure Act exemption to determine whether and to what extent it has been abused for purposes of concealing foreign influence.
Only 15 violations of FARA have been criminally prosecuted since 1966 and “about half of those stemmed from Mr. Mueller’s investigation,” according to Grassley’s statement in his press release.
Co-sponsors of the bill include Democratic Sens. Jeanne Shaheen and Dianne Feinstein.
June 8, 2018 •
FARA Advisory Opinions Now Available to Public
On June 8, the Department of Justice’s (DOJ) Foreign Agents Registration Act (FARA) Registration Unit released several years’ worth of advisory opinions previously unavailable to the public. The advisory opinions, covering the period from January 1, 2010, to the present, […]
 On June 8, the Department of Justice’s (DOJ) Foreign Agents Registration Act (FARA) Registration Unit released several years’ worth of advisory opinions previously unavailable to the public.
On June 8, the Department of Justice’s (DOJ) Foreign Agents Registration Act (FARA) Registration Unit released several years’ worth of advisory opinions previously unavailable to the public.
The advisory opinions, covering the period from January 1, 2010, to the present, had been previously issued to individuals and lobbyists concerning registration and other issues falling under FARA. 49 advisory opinions concerning FARA have been issued by the DOJ since January 1, 2010.
Also included with the release of the advisory opinions are three additional letters sent in response to requests for general information.
Future advisory opinions will be made publicly available and posted on the DOJ’s website periodically.
March 27, 2018 •
Foreign Influence Transparency Act Introduced in Senate
On March 21, Senators Marco Rubio and Tom Cotton and Rep. Joe Wilson introduced a bill to limit exemptions for registration under the Foreign Agents Registration Act (FARA). Senate Bill 2583, the Foreign Influence Transparency Act, amends FARA to limit […]
 On March 21, Senators Marco Rubio and Tom Cotton and Rep. Joe Wilson introduced a bill to limit exemptions for registration under the Foreign Agents Registration Act (FARA).
On March 21, Senators Marco Rubio and Tom Cotton and Rep. Joe Wilson introduced a bill to limit exemptions for registration under the Foreign Agents Registration Act (FARA).
Senate Bill 2583, the Foreign Influence Transparency Act, amends FARA to limit the exemption from the registration requirements for persons engaging in activities in furtherance of bona fide religious, scholastic, academic, or scientific pursuits or the fine arts to activities which do not promote the political agenda of a foreign government.
The bill limits the existing registration exemptions by qualifying they apply “only if the activities do not promote the political agenda of a government of a foreign country.” The legislation also amends the Higher Education Act of 1965 by requiring the disclosures of foreign gifts and contracts over $50,000 made to universities.
“The goal of this legislation is to increase transparency between foreign governments, universities, and communities,” said Wilson in his press release.
On March 1, a bill was introduced in the U.S. Senate to amend the Foreign Agents Registration Act (FARA). Included in the bipartisan bill, the Foreign Agents Registration Amendments Act, are the creation of an enforcement unit in the National […]
 On March 1, a bill was introduced in the U.S. Senate to amend the Foreign Agents Registration Act (FARA).
On March 1, a bill was introduced in the U.S. Senate to amend the Foreign Agents Registration Act (FARA).
Included in the bipartisan bill, the Foreign Agents Registration Amendments Act, are the creation of an enforcement unit in the National Security Division and updates to civil and criminal enforcement procedures. The legislation also creates a definition for the term ‘‘operative of a foreign government.”
Additionally, the bill would call for self-identification of registered individuals when meeting with members of congress or their staff.
Specifically, the bill states, “It shall be unlawful for any agent of a foreign principal registered under [FARA] to fail to disclose before or during any meeting with a member of Congress or staff of a member of Congress that the agent has registered under [FARA].’’
The bill was introduced by Republican Senators Todd Young and John Cornyn and Democratic Senators Dianne Feinstein and Jeanne Shaheen.
State and Federal Communications, Inc. provides research and consulting services for government relations professionals on lobbying laws, procurement lobbying laws, political contribution laws in the United States and Canada. Learn more by visiting stateandfed.com.

